| Medicinal Values |
 |
- Senna is an excellent laxative.
- Senna is employed in treating many other ailments like, anemia, typhoid, cholera, jaundice, rheumatism, gout, tumours, probably in leprosy, in splenic enlargement, foul breath and bronchitis.
- It is also used in the treatment of amoebic dysentery and a mild liver stimulant.
- Effective in constipation, thermogenic, cathartic, liver tonic, abdominal disorders, leucoderma, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, dyspepsia, cough and skin disorders.
- Sennoside acts on the lower bowel and is especially useful in improving / lightening constipation.
Pharmacology
- It is a soft purgative because of the presence of ample Anthraquinone.
- Senna is still used as the primary ingredient in certain commercial stimulant laxatives.
- Senna is also the primary ingredient found in most "dieter's teas". The combination of acting as a stimulant which reduces a dieter's appetite, and the laxative properties that cause food to move through their system before as many calories can be absorbed is a combination that can lead to rapid weight loss.
- It increases the peristaltic movements of the colon by its local action upon the intestinal wall. Its active principle must pass out of the system in the secretions unaltered. The purgative effect is increased by the addition of pure bitters.
Principle Constituents
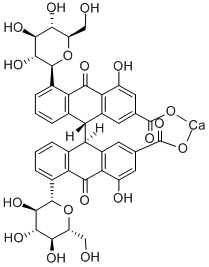
- Senna acts as purgative and has active ingredients Anthraquinone derivatives and their glucosides. The latter are called Sennosides or senna glycosides. It increases the peristaltic movements of the colon.
- The purgative constituents are closely allied to those of Aloes and Rhubarb, the activities of the drug being largely due to Anthraquinone derivatives and their glucosides. It contains Rhein, Rhein 8-glucoside, Rhein 8-diglucoside, 8-glucoside, kaempferol, aloe-emedin, Isorhamnetin, both free and as glucosides together with myricyl alcohol, Chrysophanic Acid, etc.
- The ash amounts to about 8 per cent, consisting chiefly of earthy and ashy carbonates.
|
|
|
|